
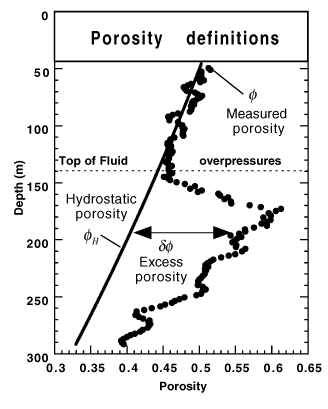
Figure 2. Definitions of the porosity parameters introduced in the model. The hydrostatic porosity distribution,  H, is the porosity distribution resulting from equilibrium compaction (i.e., no pore fluid overpressures are generated). The function
H, is the porosity distribution resulting from equilibrium compaction (i.e., no pore fluid overpressures are generated). The function  H = f (z) is called the "(hydrostatic) normal trend of compaction." The measured porosity,
H = f (z) is called the "(hydrostatic) normal trend of compaction." The measured porosity,  , is equal to
, is equal to  H only in the hydrostatically pressured formations. The case
H only in the hydrostatically pressured formations. The case  >
>  H corresponds to undercompacted formations. The case
H corresponds to undercompacted formations. The case  <
<  H corresponds to overcompacted formation. If fluid overpressures result from a compaction disequilibrium process, the difference
H corresponds to overcompacted formation. If fluid overpressures result from a compaction disequilibrium process, the difference  -
-  H =
H = 
 is called the "excess porosity" and can be directly related to the fluid overpressure
is called the "excess porosity" and can be directly related to the fluid overpressure  p.
p.

 H, is the porosity distribution resulting from equilibrium compaction (i.e., no pore fluid overpressures are generated). The function
H, is the porosity distribution resulting from equilibrium compaction (i.e., no pore fluid overpressures are generated). The function  H = f (z) is called the "(hydrostatic) normal trend of compaction." The measured porosity,
H = f (z) is called the "(hydrostatic) normal trend of compaction." The measured porosity,  , is equal to
, is equal to  H only in the hydrostatically pressured formations. The case
H only in the hydrostatically pressured formations. The case  >
>  H corresponds to undercompacted formations. The case
H corresponds to undercompacted formations. The case  <
<  H corresponds to overcompacted formation. If fluid overpressures result from a compaction disequilibrium process, the difference
H corresponds to overcompacted formation. If fluid overpressures result from a compaction disequilibrium process, the difference  -
-  H =
H = 
 is called the "excess porosity" and can be directly related to the fluid overpressure
is called the "excess porosity" and can be directly related to the fluid overpressure  p.
p.

![]()