ANALYTICAL METHODS
We investigated a total of 18 core samples from Hole 977A (Table 1). After freeze-drying and grinding, the sediments were analyzed for total carbon (TC) content coulometrically in a Ströhlein Coulomat 702. Carbonate contents were determined after acidification as carbon dioxide using a UIC-Coulometrics CM 5012 device. Total organic carbon (TOC) content was calculated as the difference between total and inorganic carbon contents.
Dry sediment (4 g) was extracted with a dichloromethane/1% methanol (v/v) mixture four times (once at 50 mL followed by three times at 30 mL) in an ultrasonic bath. The combined decanted extracts were concentrated by rotary evaporation to 2 mL and dried in a stream of nitrogen at mild temperature (30°-35°C). Extract yields were determined gravimetrically. Elemental sulfur was removed from the total extracts with activated copper filings.
Separation of the extracts into fractions of different polarities was carried out after addition of internal standards (squalane, anthracene-d10, 5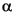 -androstan-17-one, 5
-androstan-17-one, 5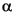 androstan-3ß-ol and erucic acid [n-C22:1 fatty acid]). Before column chromatographic separation, the asphaltenes were precipitated by adding an excess of n-hexane. The n-hexane-soluble portion was separated by medium-pressure liquid chromatography (MPLC; Radke et al., 1980) into fractions of nonaromatic hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, and heterocompounds (NSO fraction).
androstan-3ß-ol and erucic acid [n-C22:1 fatty acid]). Before column chromatographic separation, the asphaltenes were precipitated by adding an excess of n-hexane. The n-hexane-soluble portion was separated by medium-pressure liquid chromatography (MPLC; Radke et al., 1980) into fractions of nonaromatic hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, and heterocompounds (NSO fraction).
Subsequently, ketones, esters, and n-alkanols (>C20) were separated from the more polar NSO fraction by flash chromatography (Still et al., 1978). For this purpose, a 10- x 200-mm column was filled with 5 g of silica gel 60 (40-63 µm, deactivated with 5% by weight of water) and washed with 50 mL dichloromethane. The less polar fraction was eluted with 60 mL dichloromethane under a moderate overpressure of nitrogen. The other compounds were removed from the column with 100 mL of a mixture of dichloromethane and 10% by volume of methanol. The polar portion of the NSO fraction was separated into an acid fraction and a steroid alcohol fraction using a column filled with KOH-impregnated silica gel (McCarthy and Duthie, 1962; modified after Hinrichs et al., 1995). All fractions were concentrated as described for the whole extracts and weighed. For analysis of the molecular constituents, the hetero compound fractions were silylated with N-methyl-N-trimethylsilyl-trifluoroacetamide (MSTFA).
Gas chromatography was conducted on a Hewlett-Packard 5890 Series II instrument equipped with a temperature-programmed cold-injection system (Gerstel KAS 3) and a fused silica capillary column (J&W DB-5; length = 30 m, inner diameter = 0.25 mm, film thickness = 0.25 µm). Helium was used as the carrier gas, and the temperature of the oven was programmed from 60°C (1 min isothermal) to 305°C (50 min isothermal) at a rate of 3°C/min.
GC/MS studies were performed with the same type of gas chromatograph (helium as carrier gas) and a temperature program from 60°C (1 min isothermal) to 300°C (50 min isothermal) at a rate of 3°C/min. The gas chromatograph was coupled to a Finnigan SSQ 710B mass spectrometer operated at 70 eV. Structural assignments of individual compounds are based on comparison of relative gas chromatographic retention times and mass spectra with those reported in the literature. Quantification was performed relative to the amount of internal standards with mass correction for trimethylsilylated compounds.
All ten samples from Section 161-977A-9H-5 were analyzed for lignin phenols by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The lignin phenols were released from the macromolecular organic matter as copper oxide (CuO) oxidation products following the method of Hedges and Parker (1976), modified by Eggers (1994) and refined by J. Lobbes (pers. comm., 1996). Dry sediment (0.5-1.0 g), mixed with CuO (0.5 g) and ammoniumferro(II)-sulfate hexahydrate, was heated in teflon bombs (3 hr, 150°C) after the addition of 5 mL 2 N sodium hydroxide solution. The suspensions were acidified with hydrochloric acid (30%) and extracted with diethylether (5 mL). These extracts were directly analyzed on a DAD L-4500 HPLC instrument (Merck/Hitachi).

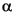 -androstan-17-one, 5
-androstan-17-one, 5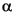 androstan-3ß-ol and erucic acid [n-C22:1 fatty acid]). Before column chromatographic separation, the asphaltenes were precipitated by adding an excess of n-hexane. The n-hexane-soluble portion was separated by medium-pressure liquid chromatography (MPLC; Radke et al., 1980) into fractions of nonaromatic hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, and heterocompounds (NSO fraction).
androstan-3ß-ol and erucic acid [n-C22:1 fatty acid]). Before column chromatographic separation, the asphaltenes were precipitated by adding an excess of n-hexane. The n-hexane-soluble portion was separated by medium-pressure liquid chromatography (MPLC; Radke et al., 1980) into fractions of nonaromatic hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, and heterocompounds (NSO fraction).