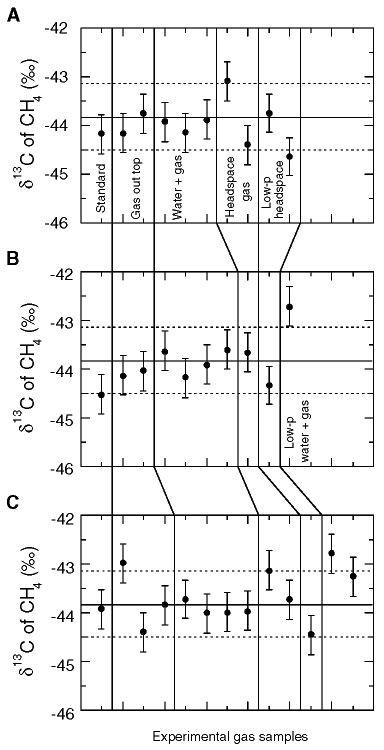
Figure 11.
Methane ![]() 13C
values of gas samples from experiments on degassing of CH4-saturated
water. Data are in Table 3.
"Standard" refers to a sample of gas that was isolated at pressure in
the T above the inlet port to the pressure vessel while the vessel was
equilibrating (see Fig. 9).
This gas was released into a syringe before the samples of headspace gas and CH4-saturated
water were taken. Similarly, "gas out top" refers to high-pressure
methane that was extracted from the pressure vessel through the vertical portion
of the inlet tube after the "standard" sample was taken. "Water +
gas" refers to CH4-saturated water extracted out of the top of
the inlet port. This water effervesced vigorously as it entered the syringes,
and all gas released from solution was trapped in the syringe. "Headspace
gas" is a sample of gas that was isolated in the sampling tube (see Fig.
9) before release of CH4-saturated water. This gas was
released into the bubbling chamber where it could be sampled using syringes.
Release of CH4-saturated water caused a large pressure drop inside
the pressure vessel. Several minutes after this pressure drop occurred, a new
sample of headspace gas (which undoubtedly contained some CH4 just
released from solution) was isolated in the sampling tube and then released to
the bubbling chamber. In the second and third experimental runs (B and C), an
additional sample of CH4-saturated water at lower pressure was
released out the top of the inlet port. The average (±2s uncertainty) CH4
13C
values of gas samples from experiments on degassing of CH4-saturated
water. Data are in Table 3.
"Standard" refers to a sample of gas that was isolated at pressure in
the T above the inlet port to the pressure vessel while the vessel was
equilibrating (see Fig. 9).
This gas was released into a syringe before the samples of headspace gas and CH4-saturated
water were taken. Similarly, "gas out top" refers to high-pressure
methane that was extracted from the pressure vessel through the vertical portion
of the inlet tube after the "standard" sample was taken. "Water +
gas" refers to CH4-saturated water extracted out of the top of
the inlet port. This water effervesced vigorously as it entered the syringes,
and all gas released from solution was trapped in the syringe. "Headspace
gas" is a sample of gas that was isolated in the sampling tube (see Fig.
9) before release of CH4-saturated water. This gas was
released into the bubbling chamber where it could be sampled using syringes.
Release of CH4-saturated water caused a large pressure drop inside
the pressure vessel. Several minutes after this pressure drop occurred, a new
sample of headspace gas (which undoubtedly contained some CH4 just
released from solution) was isolated in the sampling tube and then released to
the bubbling chamber. In the second and third experimental runs (B and C), an
additional sample of CH4-saturated water at lower pressure was
released out the top of the inlet port. The average (±2s uncertainty) CH4
![]() 13C
of methane used in the experiments, based on data from the pressurized methane
release experiments (Table 2; Fig.
10), is shown by the solid and dashed lines.
13C
of methane used in the experiments, based on data from the pressurized methane
release experiments (Table 2; Fig.
10), is shown by the solid and dashed lines.
![]()