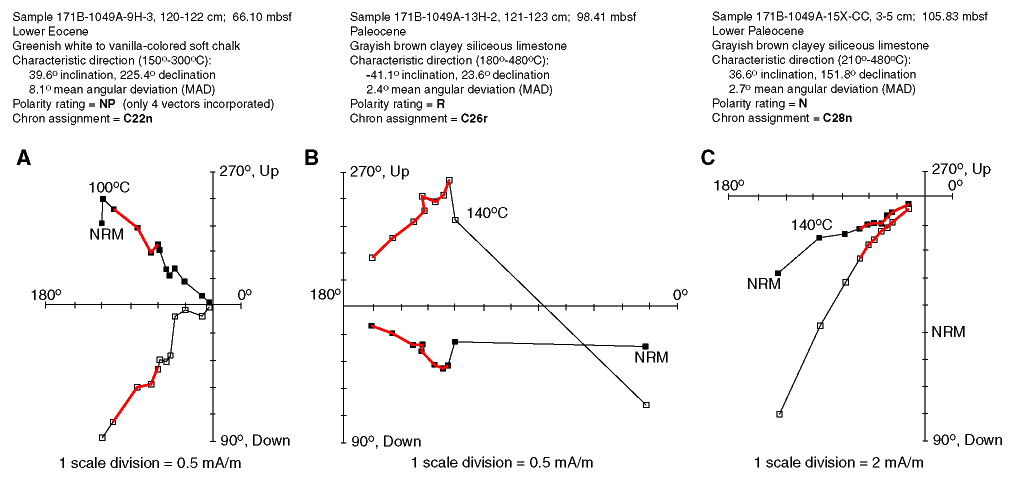
Figure F1. Representative vector plots of thermal demagnetization, characteristic directions, and polarity ratings for Paleogene samples from Hole 1049A. Declination (solid squares) is relative to a perpendicular line into the cut face of the working half of the core and is projected onto a horizontal plane, and inclination (open squares) is the actual value and magnitude. The bold line is the succession of vectors used to compute the characteristic direction for each sample. A. Eocene chalk at 50°C heating steps between 100° and 650°C; characteristic direction is assigned an NP polarity rating because it is computed from only four vectors. B. Paleocene siliceous limestone at 140°C, then 30°C heating steps between 180° and 300°C, then 350°, 400°, and 480°C; characteristic direction is assigned an R polarity rating because it is computed from eight vectors with a low mean angular deviation. C. Paleocene siliceous limestone with the same demagnetization as in B; characteristic direction is assigned an N polarity rating because it is computed from seven vectors with a low mean angular deviation.
![]()