8. Origin and Age of Submarine Ferromanganese Hardgrounds from the Marion Plateau, offshore Northeast Australia1
P.R. Heck,2,
3,
4 M. Frank,3,
5 F.S. Anselmetti,4 and P.W. Kubik6
ABSTRACT
Be and Nd isotope compositions and metal concentrations (Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, and Cu) of surface and subsurface ferromanganese hardground crusts from Ocean Drilling Program Leg 194 Marion Plateau Sites 1194 and 1196 provide new insights into the crusts' genesis, growth rates, and ages. Metal compositions indicate that the hardgrounds, which have grown on erosional surfaces in water depths of <400 m because of strong bottom currents, are not pure hydrogenetic precipitates. Nevertheless, the ratios between cosmogenic 10Be and stable 9Be in hardgrounds from the present-day seafloor at Site 1196 between 1 x 10–7 and 1.5 x 10–7 are within the range of values expected for Pacific seawater, which shows that the hardgrounds recorded the isotope composition of ambient seawater. This is also confirmed by their Nd isotope composition (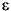 Nd between –3 and 0). The 10Be/9Be ratios in the up to 30-mm-thick and partly laminated hardgrounds do not show a decrease with depth, which suggests high growth rates on the present-day seafloor. The subsurface crust at Site 1194 (117 m below the seafloor) grew during a sedimentation hiatus, when bottom currents in the late Miocene prevented sediment accumulation on the carbonate platform during a sea level lowstand. The age of 8.65 ± 0.50 Ma for this crust obtained from 10Be-based dating agrees well with the combined seismostratigraphic and biostratigraphic evidence, which suggests an age for the hiatus between 7.7 and 11.8 Ma.
Nd between –3 and 0). The 10Be/9Be ratios in the up to 30-mm-thick and partly laminated hardgrounds do not show a decrease with depth, which suggests high growth rates on the present-day seafloor. The subsurface crust at Site 1194 (117 m below the seafloor) grew during a sedimentation hiatus, when bottom currents in the late Miocene prevented sediment accumulation on the carbonate platform during a sea level lowstand. The age of 8.65 ± 0.50 Ma for this crust obtained from 10Be-based dating agrees well with the combined seismostratigraphic and biostratigraphic evidence, which suggests an age for the hiatus between 7.7 and 11.8 Ma.
1Heck, P.R., Frank, M., Anselmetti, F.S., and Kubik, P.W., 2007. Origin and age of submarine ferromanganese hardgrounds from the Marion Plateau, offshore northeast Australia. In Anselmetti, F.S., Isern, A.R., Blum, P., and Betzler, C. (Eds.), 2006, Proc. ODP, Sci. Results, 194: College Station, TX (Ocean Drilling Program), 1–22. doi:10.2973/odp.proc.sr.194.008.2007
2Max-Planck-Institute for Chemistry, Particle Chemistry Department, Becherweg 27, D-55128 Mainz, Germany. heck@mpch-mainz.mpg.de
3Institute for Isotope Geology and Mineral Resources, NW C84, ETH Zurich, CH-8092 Zurich, Switzerland.
4Geological Institute, ETH Zurich, CH-8092 Zurich, Switzerland.
5IFM-GEOMAR, Leibniz Institute for Marine Sciences, University of Kiel, Wischhofstrasse 1-3, 24184 Kiel, Germany.
6Paul Scherrer Institute, c/o Institute for Particle Physics, ETH Zurich, CH-8093 Zurich, Switzerland.
Initial receipt: 9 March 2004
Acceptance: 20 October 2006
Web publication:
30 March 2007
Ms 194SR-008

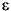 Nd between –3 and 0). The 10Be/9Be ratios in the up to 30-mm-thick and partly laminated hardgrounds do not show a decrease with depth, which suggests high growth rates on the present-day seafloor. The subsurface crust at Site 1194 (117 m below the seafloor) grew during a sedimentation hiatus, when bottom currents in the late Miocene prevented sediment accumulation on the carbonate platform during a sea level lowstand. The age of 8.65 ± 0.50 Ma for this crust obtained from 10Be-based dating agrees well with the combined seismostratigraphic and biostratigraphic evidence, which suggests an age for the hiatus between 7.7 and 11.8 Ma.
Nd between –3 and 0). The 10Be/9Be ratios in the up to 30-mm-thick and partly laminated hardgrounds do not show a decrease with depth, which suggests high growth rates on the present-day seafloor. The subsurface crust at Site 1194 (117 m below the seafloor) grew during a sedimentation hiatus, when bottom currents in the late Miocene prevented sediment accumulation on the carbonate platform during a sea level lowstand. The age of 8.65 ± 0.50 Ma for this crust obtained from 10Be-based dating agrees well with the combined seismostratigraphic and biostratigraphic evidence, which suggests an age for the hiatus between 7.7 and 11.8 Ma.