
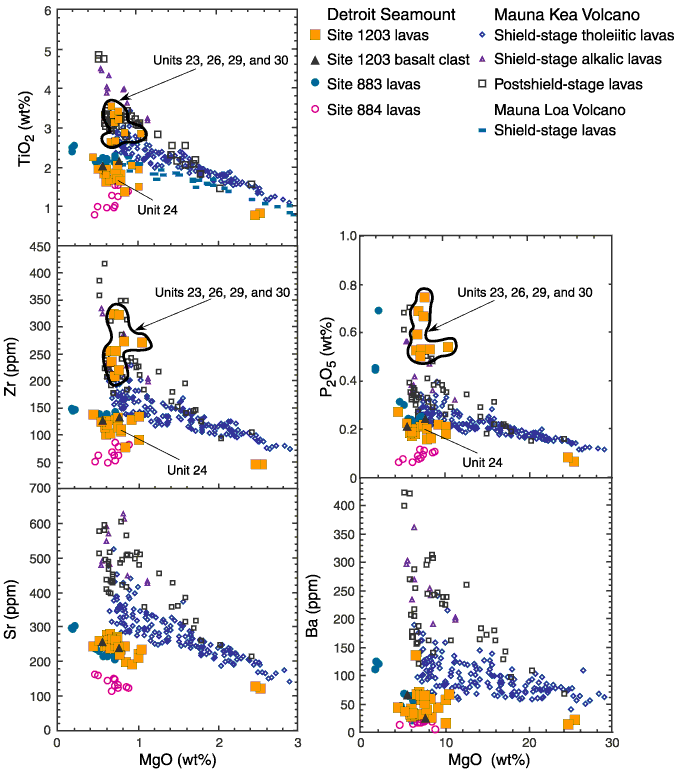
Figure F46. Abundances of TiO2, P2O5, Zr, Sr, and Ba vs. MgO in Detroit Seamount lavas compared to lavas from Mauna Kea and Mauna Loa Volcanoes (only the TiO2 panel shows the Mauna Loa lavas). Data sources are given in the caption for Figure F42. At a given MgO content in the TiO2, P2O5, and Zr panels, Site 884 lavas have much lower abundances of these incompatible elements than lavas from volcanoes on the island of Hawaii. The range of TiO2 in Hawaiian shield-stage lavas is indicated by the variation from Mauna Loa to Mauna Kea Volcano. Site 883 lavas have slightly lower contents of these elements than the Mauna Loa and Mauna Kea shield-stage lavas. The Site 1203 transitional to tholeiitic lavas, including the two picritic lavas, largely fill the gap between lavas from Sites 883 and 884. In contrast, alkalic basalt from Units 23, 26, 29, and 30 at Site 1203 has high concentrations of these elements and overlaps with the field for postshield-stage lavas from Mauna Kea Volcano. In the Sr and Ba panels, however, this alkalic basalt is not distinguished by higher Ba and Sr contents (except for anomalous Sample 197-1203-51R-4, 93-95 cm). Also see Figure F45.


![]()