 Lamptonium
fabaeforme fabaeforme (Krasheninnikov)
Lamptonium
fabaeforme fabaeforme (Krasheninnikov) Lamptonium
fabaeforme fabaeforme (Krasheninnikov)
Lamptonium
fabaeforme fabaeforme (Krasheninnikov)[?] Cyrtocalpis fabaeformis Krasheninnikov, 1960, p.296, pl.3, fig.11
Lamptonium(?) fabaeforme fabaeforme (Krasheninnikov), Riedel and Sanfilippo, 1970, p.523, pl.5, fig.6; Foreman, 1973, p.436, pl.6, figs.6-9
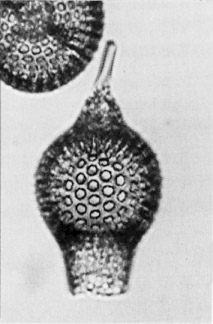
Cephalis spherical, surrounded by the thick wall continuing upward from the thorax, bearing a conical or bladed horn of variable length. Thorax inflated-pyriform, with rough or thorny surface, and with circular or subcircular pores that are largest in the midregion. Abdomen short, narrow, subcylindrical or tapering, with irregularly scattered pores and no differentiated termination (Foreman, 1973).
Length excluding horn 150-285 µm; of cephalothorax 125-200 µm. Maximum breadth 100-170 µm.
Thorax elongated, inflated pyriform without lateral spines. Abdomen much narrower than thorax, subcylindrical or tapering distally (Riedel and Sanfilippo, 1978a)
L. f. fabaeforme differs from its ancestor L. pennatum in lacking thoracic wings, and from L. f. chaunothorax in having smaller thoracic pores. L. f. fabaeforme has at least twelve pores across the half circumference of the thorax (Sanfilippo et al., 1985).
This three-segmented form has a spherical cephalis, enclosed in the thick wall continuing upward from the thorax, bearing a bladed or conical horn of variable length. In early forms the thorax is somewhat smaller than in later ones, and nodose rather than thorny. The pores are circular to subcircular, largest in the mid-region, and frequently with an uneven margin. The subcylindrical to tapering abdomen has scattered, irregular pores and an undifferentiated margin (Sanfilippo et al., 1985).
Lamptonium f. fabaeforme is found in early to early middle Eocene assemblages from 35°S to 35°N, except at DSDP Site 366 where the assemblages are sparse (other members of the genus occur there). It evolved from Lamptonium pennatum within the Bekoma bidartensis Zone. Its morphotypic last appearance lies within the Dictyoprora mongolfieri Zone.
L. f. fabaeforme developed from L. pennatum, and gave rise to L. f. chaunothorax.