Porosity is given by
where Vw is the volume of water contained in the sample and Vg is the volume of solid in the sample (Boyce, 1973). Porosity at atmospheric pressure was measured in samples taken adjacent to those used in the shore-based study. The initial water and solid volumes are given by
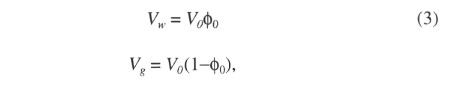
where ![]() 0 is the porosity at atmospheric pressure measured shipboard and V0 is the initial volume of the sample determined from caliper measurements of the sample dimensions prior to testing. Assuming the volume loss under pressure is due solely to a reduction in pore space, the porosity under pressure is given by
0 is the porosity at atmospheric pressure measured shipboard and V0 is the initial volume of the sample determined from caliper measurements of the sample dimensions prior to testing. Assuming the volume loss under pressure is due solely to a reduction in pore space, the porosity under pressure is given by
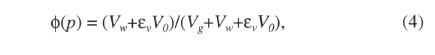
where ![]() v is the volumetric strain the sample undergoes during the pressure testing (the sign convention is that compression is negative). The in situ porosity is determine from
Eq. 4 using the estimated in situ effective pressure. Assuming that strain is isotropic, the volumetric strain can be determined by linearly interpolating the sample shortening as discussed previously, applying an equal percentage of shortening in the vertical and horizontal dimensions. The estimated in situ porosity is plotted as a function of depth in
Figure 7. The porosity is generally consistent with an exponential relationship similar to that used in other studies (e.g., Sclater and Christie, 1980):
v is the volumetric strain the sample undergoes during the pressure testing (the sign convention is that compression is negative). The in situ porosity is determine from
Eq. 4 using the estimated in situ effective pressure. Assuming that strain is isotropic, the volumetric strain can be determined by linearly interpolating the sample shortening as discussed previously, applying an equal percentage of shortening in the vertical and horizontal dimensions. The estimated in situ porosity is plotted as a function of depth in
Figure 7. The porosity is generally consistent with an exponential relationship similar to that used in other studies (e.g., Sclater and Christie, 1980):
where ![]() s is the porosity at the seafloor. However, the large scatter in the data and the limited number of data points result in large variance in the fit. A least squares fit of
Eq. 5 to the calculated in situ porosity yields c = 0.00064 m-1 and
s is the porosity at the seafloor. However, the large scatter in the data and the limited number of data points result in large variance in the fit. A least squares fit of
Eq. 5 to the calculated in situ porosity yields c = 0.00064 m-1 and
![]() s = 0.52 with a correlation coefficient of 0.19. If
s = 0.52 with a correlation coefficient of 0.19. If
![]() s is assumed to be 1, the least squares fit gives c = 0.02957 m-1 with a correlation coefficient of 0.71. Curves showing both least-squares fits are shown in
Figure 7.
s is assumed to be 1, the least squares fit gives c = 0.02957 m-1 with a correlation coefficient of 0.71. Curves showing both least-squares fits are shown in
Figure 7.
By mass balance, density is given by
where ![]() g is the grain density (measured shipboard) and
g is the grain density (measured shipboard) and
![]() w is the density of seawater. The calculated in situ density is shown in
Figure 8, and it can be reasonably described by a linear increase in density with depth:
w is the density of seawater. The calculated in situ density is shown in
Figure 8, and it can be reasonably described by a linear increase in density with depth:
where density is in g/cm3 and z is depth in meters.